What is a star?
Look up in the night sky and you’ll see lots of stars. But what is a star? In a scientific sense, a star is ball of hydrogen and helium with enough mass that it can sustain nuclear fusion at its core. Our Sun is a star, of course, but stars can come in different sizes and colors. So let’s learn what a star is.

Life Cycle as a star
The life cycle of a star depends on how big the star is as well as many other factors. Take a look at the picture below to get a general idea of the life cycle of a star.
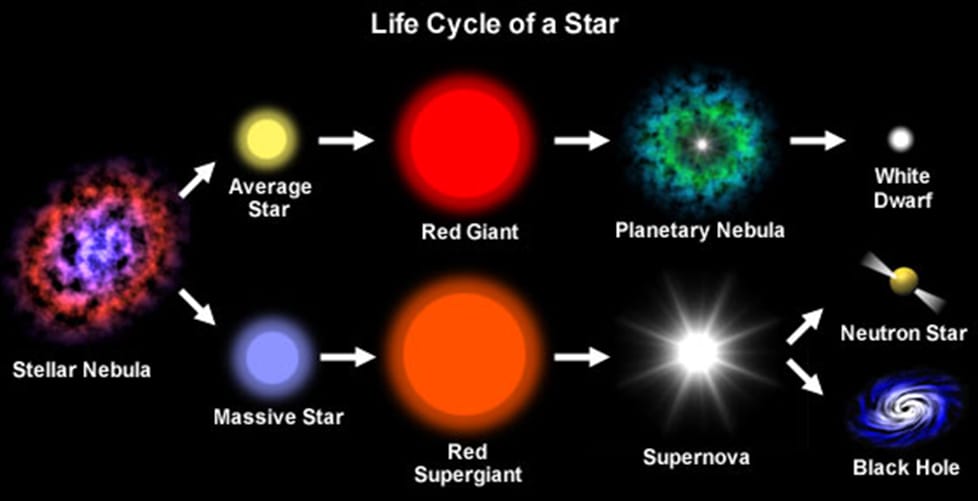
Small stars and massive stars have different life cycles.
Both stars are born from nebulae called molecular clouds. When they gravitationally collapse, they form a star from the gases in the cloud.

The Crab nebula
Small and Medium stars
Stars sustain a reaction called nuclear fusion at its core to keep it radiating heat and energy. Eventually, it will run out of its fuel, which is made up of the gases hydrogen and helium. What happens to the star then? That depends on its size.
Small stars will become Red Giants after 10 billion years. It first runs out of hydrogen and stars fusing helium. This causes the star to expand to a Red giant.
Eventually, this star will also run out of helium. The star will then try to incorporate the non-combinable element carbon, which will cause the gases from the surface of the star to dissipate. This leaves behind a blinding white, carbon-dense white dwarf star.

A Red Giant
Massive Stars
Massive stars often burn with a bright blue glow due to their intense heat. When they run out of hydrogen, they expand and begin to make all different kinds of elements until it start forming iron.
When the star only has iron left, gravity will collapse the star until it explodes from the pressure. This causes what we know as the supernova, a gigantic explosion of hot gases from the star.
After the supernova, a star can do two things:
It can become a really dense neutron star, or it can become an even denser black hole.
In both cases, when stars die, they release gases that form nebulas, which then give birth to new stars! And so the life cycle of the star begins again.

Massive Star

Supernova

Neutron star

Black hole
Our Sun as a Star

The sun is a hot ball of glowing gases, and it exists in the heart of our solar system. Its influence extends far beyond the orbits of distant Neptune and Pluto. Without the sun's intense energy and heat, there would be no life on Earth. And though it is special to us, there are billions of stars like our sun scattered across the Milky Way galaxy.
Did you know:

Some of the stars in the sky you see are actually long gone. How can this be? Light travels extremely fast, but space is so vast that it takes many years for the light from distant stars to travel to Earth so we can see them. Some of the stars that have already long died have light that is still traveling to us on Earth. How cool is that?
Exercise
Open the exercise to begin the activity. Follow the instructions in the document.